Voltage of Car Battery When Off
Understanding the voltage of car battery when off is essential for diagnosing health and preventing unexpected breakdowns. A fully charged battery should read between 12.6 and 12.8 volts when the engine is off—anything lower may signal a weak or discharged battery.
You’ve probably been there—turning the key, hearing that dreaded clicking sound, and realizing your car won’t start. More often than not, the culprit is a weak or dead battery. But how can you tell if your battery is healthy before it leaves you stranded? The answer lies in understanding the voltage of car battery when off.
Unlike when the engine is running (where the alternator keeps voltage around 13.7–14.7 volts), a car battery at rest tells a much clearer story about its true condition. When the car is completely off—no lights, no radio, no accessories drawing power—the battery’s voltage reflects its state of charge. This resting voltage is one of the simplest yet most reliable ways to assess battery health without specialized tools or a trip to the mechanic.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about measuring, interpreting, and maintaining your car battery’s voltage when the engine is off. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or just want to avoid surprise breakdowns, knowing what your battery’s voltage means can save you time, money, and stress.
In This Article
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 📑 Table of Contents
- 3 What Is Car Battery Voltage and Why Does It Matter?
- 4 How to Measure Car Battery Voltage When Off
- 5 What Affects Car Battery Voltage When Off?
- 6 Interpreting Your Voltage Reading: What’s Normal?
- 7 How to Maintain Healthy Battery Voltage
- 8 When to Replace Your Car Battery
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
- 10.1 What should a car battery read when the engine is off?
- 10.2 Is 12.4 volts OK for a car battery?
- 10.3 Can a car battery show 12.6 volts and still be bad?
- 10.4 Why does my battery voltage drop when the car is off?
- 10.5 How long should I wait to test battery voltage after turning off the car?
- 10.6 Does cold weather affect car battery voltage?
Key Takeaways
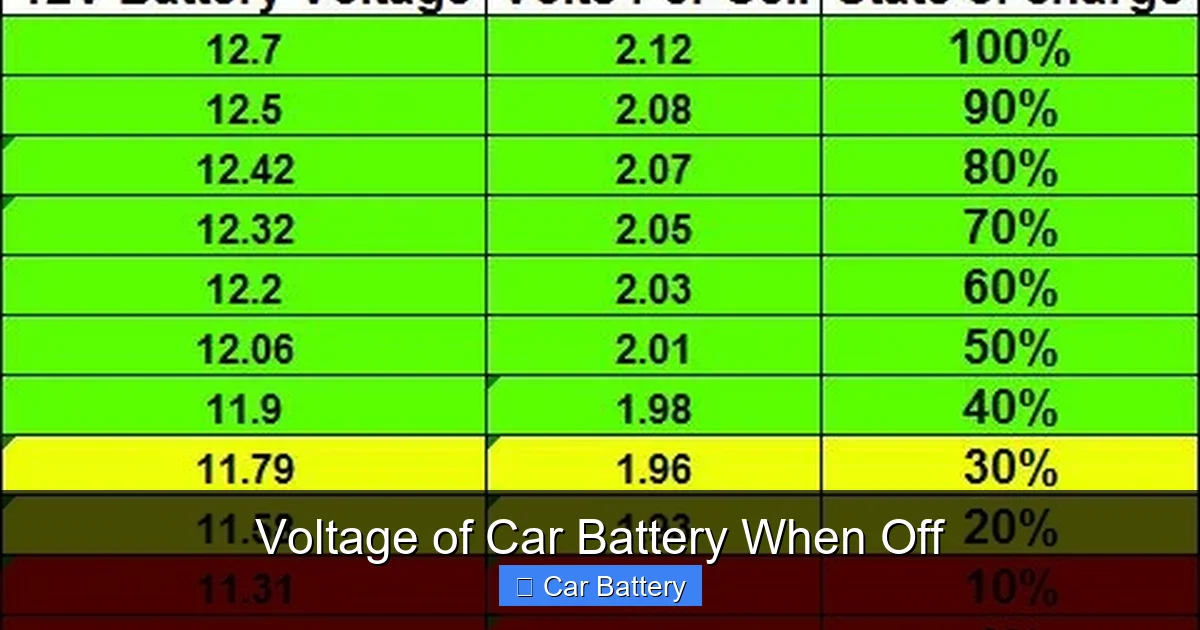
- Normal resting voltage: A healthy car battery reads 12.6–12.8 volts when the engine is off and the car has been sitting for at least an hour.
- Below 12.4 volts = low charge: Readings under 12.4 volts indicate the battery is partially discharged and may struggle to start the engine.
- Parasitic drain matters: Even when off, small electrical loads (like clocks or alarms) slowly drain the battery—over time, this can drop voltage significantly.
- Temperature affects readings: Cold weather reduces battery efficiency; a “good” voltage in winter might still result in a no-start condition.
- Use a multimeter correctly: Always test with the engine off, lights and accessories turned off, and after the car has rested for 1–2 hours for accurate results.
- Regular checks prevent failure: Testing voltage monthly helps catch issues early and extends battery life.
- Replacement threshold: If voltage consistently drops below 12.2 volts or won’t hold a charge after recharging, it’s time for a new battery.
📑 Table of Contents
What Is Car Battery Voltage and Why Does It Matter?
Car batteries are designed to deliver a steady flow of electrical current to start your engine and power accessories when the engine isn’t running. Most modern vehicles use a 12-volt lead-acid battery system, which consists of six cells connected in series. Each cell produces about 2.1 volts when fully charged, adding up to roughly 12.6 volts total.
The voltage of your car battery when off is essentially a snapshot of its energy reserve. Think of it like checking the fuel gauge in your car—except instead of gallons, you’re measuring electrical potential in volts. A high resting voltage means the battery is well-charged and ready to deliver the burst of power needed to crank the engine. A low voltage suggests the battery is depleted, aging, or possibly failing.
How Voltage Reflects Battery State of Charge
Here’s a quick reference for what different voltage readings mean when the engine is off:
- 12.6–12.8 volts: Fully charged (100% state of charge)
- 12.4 volts: About 75% charged
- 12.2 volts: Around 50% charged
- 12.0 volts or below: Less than 25% charged—likely won’t start the car
These values assume the battery has been at rest for at least one hour. Why the wait? Because immediately after driving, the battery may show a higher voltage due to surface charge—a temporary boost that fades once the chemical reactions inside stabilize.
The Role of Lead-Acid Chemistry
Most car batteries are flooded lead-acid types, though some newer models use AGM (absorbent glass mat) or lithium-ion technology. In lead-acid batteries, voltage is directly tied to the concentration of sulfuric acid in the electrolyte. When the battery discharges, sulfuric acid reacts with lead plates to produce electricity, reducing acid concentration and lowering voltage. Recharging reverses this process.
This chemical relationship is why voltage is such a reliable indicator: it’s not just an electrical reading—it’s a direct measure of the battery’s chemical energy reserve.
How to Measure Car Battery Voltage When Off
Testing your battery’s voltage is easier than you might think—and you don’t need to be a mechanic to do it. All you need is a basic digital multimeter, which you can find at any auto parts store for under $20.

Visual guide about Voltage of Car Battery When Off
Image source: cdn.shopify.com
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing
- Turn off the engine and all electrical loads. Make sure headlights, interior lights, radio, and climate control are completely off.
- Let the car sit for 1–2 hours. This allows surface charge to dissipate and gives you an accurate resting voltage.
- Set your multimeter to DC voltage (usually marked as “V~” or “V with a straight line”). Choose a range higher than 20 volts (most multimeters auto-range).
- Connect the red probe to the positive terminal (+) and the black probe to the negative terminal (–). Ensure good contact—clean terminals if they’re corroded.
- Read the display. A reading between 12.6 and 12.8 volts means your battery is in great shape.
Pro tip: If you don’t have a multimeter, many auto parts stores offer free battery testing. However, doing it yourself gives you more control and helps you learn about your vehicle’s electrical system.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Testing immediately after driving: Surface charge can give falsely high readings.
- Leaving accessories on: Even a small draw (like a trunk light) can skew results.
- Using analog meters: They’re less accurate than digital multimeters for battery testing.
- Ignoring terminal corrosion: Poor contact leads to inaccurate readings—clean terminals with baking soda and water if needed.
What Affects Car Battery Voltage When Off?
While a healthy battery should maintain 12.6+ volts at rest, several factors can cause voltage to drop—even when the car is off.

Visual guide about Voltage of Car Battery When Off
Image source: carawareness.com
Parasitic Drain
Modern cars are packed with electronics: clocks, alarms, keyless entry systems, onboard computers, and more. These devices draw a small amount of current even when the car is off—this is called parasitic drain. Normally, it’s minimal (around 20–50 milliamps), but faulty wiring, aftermarket accessories, or aging components can increase it significantly.
For example, a malfunctioning glove box light that stays on can drain a battery in just a few days. If your voltage drops below 12.4 volts after a short period of inactivity, parasitic drain could be the cause.
Temperature Effects
Battery performance is highly temperature-dependent. In cold weather, chemical reactions inside the battery slow down, reducing its ability to deliver current—even if voltage appears normal. A battery reading 12.6 volts at 32°F (0°C) may not have enough cranking power to start a cold engine.
Conversely, extreme heat accelerates internal corrosion and evaporation of electrolyte, shortening battery life. In hot climates, batteries often fail sooner, even if voltage tests look good.
Battery Age and Condition
All batteries degrade over time. A typical car battery lasts 3–5 years. As it ages, its internal plates corrode, reducing capacity and the ability to hold a charge. Even if you recharge it, an old battery may not reach full voltage or may drop quickly after charging.
Sulfation—the buildup of lead sulfate crystals on the plates—is another common issue. It occurs when a battery sits in a discharged state for too long and can permanently reduce capacity.
State of Charge vs. State of Health
It’s important to distinguish between state of charge (SoC) and state of health (SoH). Voltage tells you about SoC—how much energy is currently stored. But it doesn’t reveal SoH—how well the battery can hold that charge over time.
For instance, a weak battery might show 12.6 volts after a full charge but drop to 12.0 volts overnight due to internal resistance. Load testing (applying a simulated engine cranking load) is the best way to assess SoH, but voltage is a great first indicator.
Interpreting Your Voltage Reading: What’s Normal?
Now that you know how to measure voltage, let’s break down what your numbers really mean.

Visual guide about Voltage of Car Battery When Off
Image source: pbs.twimg.com
12.6–12.8 Volts: Excellent
This is the sweet spot. Your battery is fully charged and in good condition. If you see this reading after the car has been off for a few hours, you’re in great shape. No action needed—just keep up regular maintenance.
12.4–12.5 Volts: Fair
Your battery is about 75% charged. It should still start your car, but it’s not at peak performance. This could be due to recent short trips (not enough time to recharge), cold weather, or mild parasitic drain. Consider driving longer distances or using a trickle charger to top it off.
12.2–12.3 Volts: Low
At 50% charge, your battery is undercharged. It may struggle to start the engine, especially in cold weather. Recharge it as soon as possible using a quality battery charger. If it won’t hold a charge after recharging, the battery may be failing.
Below 12.0 Volts: Critical
A reading under 12.0 volts means the battery is deeply discharged—less than 25% charged. It likely won’t start the car and could be damaged from sulfation. Jump-starting may work temporarily, but you’ll need to recharge it fully and test its health. If it drops again quickly, replace it.
Voltage Drop Over Time
Even a healthy battery loses charge slowly over time. In ideal conditions, a fully charged battery might lose 0.1–0.2 volts per month. But in real-world scenarios—especially with parasitic drain or extreme temperatures—the drop can be much faster.
For example, if your battery reads 12.7 volts today but drops to 12.3 volts after just three days of sitting, that’s a red flag. Investigate for parasitic drain or consider replacing an aging battery.
How to Maintain Healthy Battery Voltage
Prevention is always better than repair. Here’s how to keep your battery voltage in the optimal range and extend its lifespan.
Drive Regularly and Take Longer Trips
The alternator recharges the battery while driving. Short trips (under 15 minutes) don’t give it enough time to replenish the charge used during startup. Aim for longer drives a few times a week, or use a battery maintainer if the car sits for extended periods.
Use a Battery Maintainer or Trickle Charger
If you have a classic car, RV, or vehicle that sits unused for weeks, a smart trickle charger (also called a battery tender) keeps the battery at full charge without overcharging. These devices monitor voltage and adjust output automatically—perfect for seasonal storage.
Minimize Parasitic Loads
Avoid installing aftermarket electronics that draw power when the car is off (like high-powered stereos or tracking devices). If you must add accessories, ensure they’re wired through a switched circuit or use a relay to cut power when the ignition is off.
Keep Terminals Clean
Corrosion on battery terminals increases resistance and can prevent proper charging. Clean terminals every 6–12 months with a mixture of baking soda and water, then apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly to prevent future buildup.
Test Monthly
Make it a habit to check your battery voltage once a month. Keep a log to track changes over time. A sudden drop could indicate a failing battery or electrical issue.
Replace Before It Fails
Don’t wait for a no-start situation. Most batteries give subtle signs of decline—slower cranking, dimming lights, or voltage dropping below 12.4 volts consistently. Replace your battery every 4–5 years, or sooner if you live in extreme climates.
When to Replace Your Car Battery
Even with perfect maintenance, batteries don’t last forever. Here are clear signs it’s time for a replacement:
- Voltage consistently below 12.4 volts after a full charge
- Battery won’t hold a charge overnight
- Swollen or bulging battery case (sign of overheating or internal damage)
- Age over 5 years (check the manufacture date on the label)
- Frequent jump-starts needed
- Slow engine crank, especially in cold weather
Replacing a battery is straightforward—most auto parts stores will install it for free. Choose a battery with the correct group size, cold cranking amps (CCA), and reserve capacity (RC) for your vehicle.
Conclusion
The voltage of car battery when off is a powerful diagnostic tool that every driver should understand. A simple multimeter test can reveal whether your battery is healthy, undercharged, or nearing the end of its life. By monitoring resting voltage, minimizing parasitic drain, and maintaining good charging habits, you can avoid unexpected breakdowns and get the most out of your battery.
Remember: 12.6–12.8 volts at rest is the gold standard. Anything less warrants attention. With regular checks and smart habits, you’ll keep your car starting reliably—no matter the weather or how long it’s been sitting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should a car battery read when the engine is off?
A healthy car battery should read between 12.6 and 12.8 volts when the engine is off and the car has been sitting for at least an hour. This indicates a full state of charge.
Is 12.4 volts OK for a car battery?
12.4 volts means the battery is about 75% charged—it should still start most cars, but it’s not fully charged. Consider recharging it, especially if you plan to drive in cold weather.
Can a car battery show 12.6 volts and still be bad?
Yes. Voltage only shows state of charge, not overall health. A weak or old battery may read 12.6 volts after charging but fail under load. A load test is needed to confirm health.
Why does my battery voltage drop when the car is off?
Normal parasitic drain from electronics slowly discharges the battery. If the drop is rapid (e.g., below 12.4 volts in a day), there may be excessive drain or a failing battery.
How long should I wait to test battery voltage after turning off the car?
Wait at least 1–2 hours to allow surface charge to dissipate. This ensures an accurate resting voltage reading.
Does cold weather affect car battery voltage?
Yes. Cold temperatures slow chemical reactions in the battery, reducing its ability to deliver current—even if voltage appears normal. A “good” voltage in winter may not provide enough cranking power.