How Many Amp Hours Does a Car Battery Have

Most car batteries range from 40 to 100 amp hours (Ah), depending on size, type, and vehicle needs. Understanding amp hours helps you choose the right battery and maintain optimal performance for your car.
In This Article
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 📑 Table of Contents
- 3 Understanding Amp Hours in Car Batteries
- 4 Typical Amp Hour Ratings for Car Batteries
- 5 How Amp Hours Are Measured and Tested
- 6 Factors That Affect Amp Hour Performance
- 7 Choosing the Right Amp Hour Rating for Your Vehicle
- 8 Maintaining Amp Hour Capacity
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
- 10.1 What does amp hour mean on a car battery?
- 10.2 Is a higher amp hour battery better?
- 10.3 Can I replace a 50 Ah battery with a 70 Ah one?
- 10.4 How long will a 50 Ah battery last with the engine off?
- 10.5 Do cold temperatures reduce amp hours?
- 10.6 How often should I check my battery’s amp hour capacity?
Key Takeaways
- Amp hours (Ah) measure a battery’s energy storage capacity: The higher the Ah, the longer the battery can power your vehicle’s electrical systems.
- Standard car batteries typically have 40–60 Ah: This is sufficient for most passenger cars to start the engine and run accessories.
- Trucks and larger vehicles often need 70–100 Ah: Their bigger engines and extra electronics demand more power.
- Deep-cycle batteries used in RVs or boats may exceed 100 Ah: They’re designed for sustained energy delivery, not just quick bursts.
- Amp hour ratings are measured over a 20-hour discharge period: A 50 Ah battery delivers 2.5 amps for 20 hours before dropping to 10.5 volts.
- Temperature and age affect real-world amp hour performance: Cold weather reduces efficiency, and older batteries lose capacity over time.
- Knowing your battery’s Ah helps with troubleshooting and upgrades: It ensures compatibility with your vehicle and prevents electrical issues.
📑 Table of Contents
Understanding Amp Hours in Car Batteries
When it comes to car batteries, most people focus on cold cranking amps (CCA) — that’s the power needed to start your engine in cold weather. But there’s another critical number you should know: amp hours (Ah). This measurement tells you how much energy your battery can store and deliver over time. Think of it like the fuel tank of your battery. Just as a car’s gas tank holds a certain number of gallons, a battery’s amp hour rating shows how long it can keep your car’s electronics running.
Amp hours are especially important if you use accessories like lights, radios, or phone chargers when the engine is off. If your battery has a low amp hour rating, it might drain quickly, leaving you stranded. On the other hand, a higher Ah rating means longer runtime for your devices and better overall reliability. So, whether you’re replacing a dead battery or upgrading for better performance, understanding amp hours is essential.
What Exactly Is an Amp Hour?
An amp hour (Ah) is a unit of electric charge. It represents how much current a battery can deliver over a specific period. For example, a 50 Ah battery can supply 5 amps of current for 10 hours, or 2.5 amps for 20 hours, before it’s considered fully discharged. This measurement is based on a standard test where the battery is drained slowly over 20 hours until it reaches 10.5 volts — the typical cutoff point for a 12-volt car battery.
It’s important to note that amp hours don’t measure peak power like CCA does. Instead, they reflect endurance. A high CCA battery might start your car in freezing temperatures, but if it has a low Ah rating, it might not keep your radio playing for long with the engine off. That’s why both numbers matter — CCA for starting power, and Ah for sustained energy.
Why Amp Hours Matter for Your Vehicle
Your car’s electrical system relies on the battery not just to start the engine, but also to power lights, infotainment systems, climate controls, and more. When the engine is running, the alternator takes over most of this load. But when it’s off, the battery is the sole power source. That’s where amp hours come into play.
For example, if you leave your headlights on overnight, a battery with a higher Ah rating will last longer before dying. Similarly, if you use a dash cam, GPS, or phone charger while parked, a battery with sufficient amp hours ensures these devices won’t drain it too quickly. In vehicles with advanced electronics — like hybrids or EVs — the demand for sustained power is even greater, making Ah a crucial factor.
Typical Amp Hour Ratings for Car Batteries

Visual guide about How Many Amp Hours Does a Car Battery Have
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Now that you know what amp hours are, let’s look at the numbers you’ll actually see on car batteries. Most standard 12-volt car batteries fall within a specific range, but the exact rating depends on the vehicle type, battery size, and intended use.
Standard Passenger Cars: 40–60 Ah
For the average sedan, hatchback, or compact SUV, a battery with 40 to 60 amp hours is typical. These vehicles have modest electrical demands — just enough to start the engine and run basic accessories. A 50 Ah battery, for instance, is common in many Honda, Toyota, and Ford models. It provides enough power to crank the engine and support lights, radio, and climate control for short periods when the engine is off.
This range is sufficient for most daily drivers who don’t frequently use electronics while parked. However, if you often listen to the radio with the engine off or live in a hot climate where batteries degrade faster, you might benefit from a battery on the higher end of this range.
Trucks and Larger Vehicles: 60–100 Ah
Pickup trucks, SUVs, and vans usually require more power due to larger engines and additional electrical systems. These vehicles often come with batteries rated between 60 and 100 amp hours. For example, a Ford F-150 might use a 70 Ah battery, while a heavy-duty diesel truck could need 90 Ah or more.
The extra amp hours support features like power seats, advanced infotainment systems, towing electronics, and auxiliary lights. If you use your truck for work — running tools, winches, or camping gear — a higher Ah battery ensures you won’t run out of juice mid-task.
Deep-Cycle and Specialty Batteries: 100+ Ah
While most car batteries are designed for short bursts of high power (starting), some vehicles use deep-cycle batteries that prioritize long-term energy delivery. These are common in RVs, boats, golf carts, and electric vehicles. Deep-cycle batteries often have amp hour ratings of 100 Ah or more.
For example, a typical RV house battery might be 100–200 Ah, allowing it to power lights, refrigerators, and water pumps for hours without recharging. These batteries are built to be discharged and recharged repeatedly, unlike standard car batteries, which can be damaged if deeply drained.
How Amp Hours Are Measured and Tested
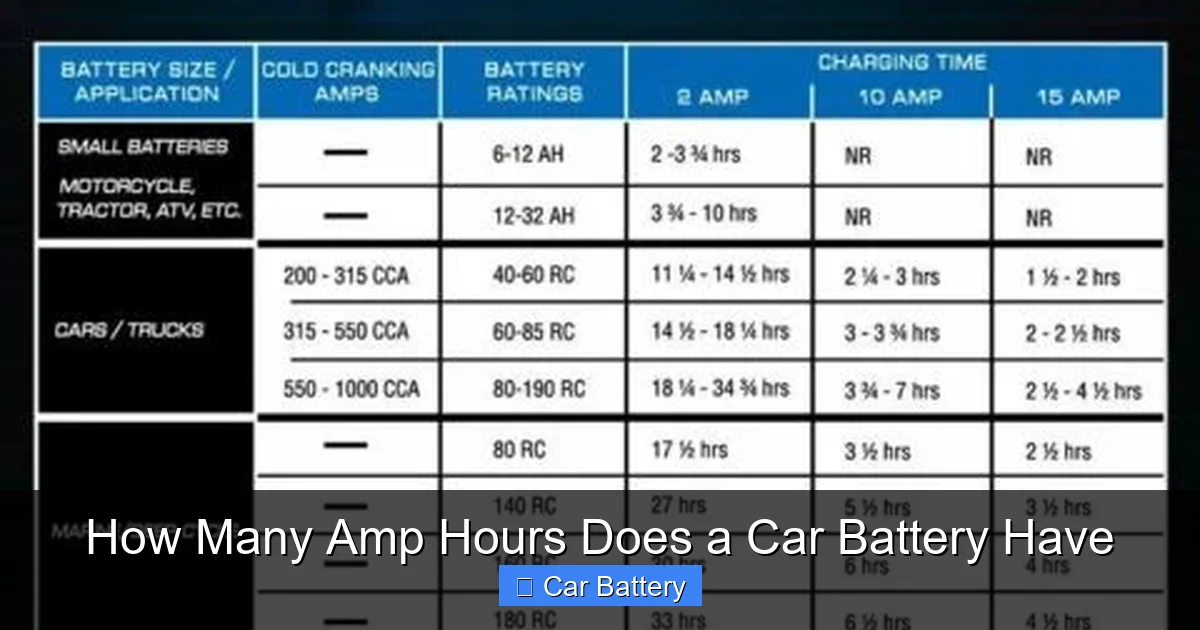
Visual guide about How Many Amp Hours Does a Car Battery Have
Image source: thepowerall.com
Understanding how amp hours are determined helps you interpret battery labels and make informed choices. The rating isn’t just a guess — it’s based on standardized testing procedures.
The 20-Hour Discharge Test
The most common method for measuring amp hours is the 20-hour discharge test. Here’s how it works: a fully charged battery is connected to a load that draws a constant current. The test continues until the battery voltage drops to 10.5 volts — the point at which it’s considered discharged.
For example, a 50 Ah battery is tested by drawing 2.5 amps (50 Ah ÷ 20 hours = 2.5 A) for 20 hours. If it lasts the full duration, it earns the 50 Ah rating. This method gives a realistic estimate of how long the battery can power low-draw devices.
Why Real-World Performance May Differ
While the 20-hour test is useful, real-world conditions often reduce performance. Temperature, battery age, and discharge rate all affect actual amp hour output. For instance, cold weather slows chemical reactions inside the battery, reducing its capacity. A 50 Ah battery might only deliver 40 Ah in freezing temperatures.
Similarly, high discharge rates — like using a high-powered inverter to run a microwave — can lower efficiency. Batteries are less effective when drained quickly. That’s why a battery might deliver 50 Ah over 20 hours but only 30 Ah if drained in 5 hours.
State of Charge and Depth of Discharge
Another factor is how deeply you discharge the battery. Most car batteries shouldn’t be drained below 50% regularly, as this shortens their lifespan. A 50 Ah battery used down to 25 Ah (50% depth of discharge) will last longer than one routinely drained to 10 Ah.
This is especially important for deep-cycle batteries, which are designed to handle deeper discharges. But even then, keeping them above 50% charge when possible extends their life.
Factors That Affect Amp Hour Performance

Visual guide about How Many Amp Hours Does a Car Battery Have
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Your battery’s amp hour rating is a starting point, but several real-world factors influence how much energy it actually delivers.
Temperature Effects
Temperature plays a huge role in battery performance. Cold weather slows down the chemical reactions that produce electricity, reducing capacity. In freezing conditions, a battery might lose 20–50% of its amp hour rating. That’s why cars struggle to start in winter — even if the battery is fully charged, it can’t deliver full power.
On the flip side, extreme heat accelerates chemical reactions but also increases internal resistance and evaporation of electrolyte. Over time, high temperatures degrade the battery faster, reducing its overall lifespan and capacity.
Battery Age and Wear
Like any component, car batteries wear out over time. Most last 3–5 years, but their amp hour capacity declines gradually. A new 50 Ah battery might only deliver 40 Ah after three years. Sulfation — the buildup of lead sulfate crystals — is a common cause of capacity loss, especially if the battery is frequently undercharged.
Regular maintenance, like keeping terminals clean and ensuring the alternator charges properly, can slow this decline. But eventually, even the best-maintained battery will need replacement.
Electrical Load and Usage Patterns
How you use your car affects how quickly the battery drains. Leaving lights on, using high-draw accessories, or frequently short trips (which don’t allow full recharge) all reduce effective amp hours.
For example, a 50 Ah battery might power a 10-watt LED light for about 60 hours (10W ÷ 12V = 0.83A; 50 Ah ÷ 0.83A ≈ 60 hours). But if you also run a 100-watt stereo, the draw increases to over 8 amps, cutting runtime to under 6 hours.
Understanding your vehicle’s electrical load helps you choose the right battery and avoid unexpected dead starts.
Choosing the Right Amp Hour Rating for Your Vehicle
Picking the correct battery isn’t just about matching the physical size — it’s about ensuring the amp hour rating meets your needs.
Check Your Owner’s Manual
The best place to start is your vehicle’s owner’s manual. It lists the recommended battery specifications, including group size, CCA, and often Ah. Following these guidelines ensures compatibility and warranty compliance.
If the manual doesn’t list Ah, look for the battery label on your current battery. It usually shows the rating along with other details like voltage and CCA.
Consider Your Driving Habits
Think about how you use your car. If you frequently drive short distances, your battery may not fully recharge, so a higher Ah rating helps compensate. Similarly, if you use accessories while parked — like a dash cam or phone charger — a battery with more amp hours provides peace of mind.
For off-grid adventures or work vehicles, consider upgrading to a deep-cycle battery with 100+ Ah. These are more expensive but offer longer runtime and better durability under heavy use.
Upgrading for Performance
Some drivers upgrade to a higher Ah battery for extra reliability. For example, swapping a 50 Ah battery for a 70 Ah model in a sedan can provide more reserve power, especially in extreme weather.
However, make sure the battery fits physically and that your alternator can handle the increased load. Most modern alternators are designed to charge standard batteries efficiently, but oversized batteries may require adjustments.
Maintaining Amp Hour Capacity
Even the best battery loses capacity over time, but proper care can slow the process.
Regular Charging
Keep your battery fully charged whenever possible. Use a smart charger if your car sits for long periods. These devices maintain optimal voltage without overcharging, preserving amp hour capacity.
Clean Terminals and Connections
Corrosion on battery terminals increases resistance, reducing efficiency. Clean them regularly with a baking soda and water solution, and apply a protective spray to prevent future buildup.
Avoid Deep Discharges
Try not to drain your battery below 50% regularly. If you accidentally leave lights on, recharge the battery as soon as possible to prevent sulfation.
Monitor Battery Health
Use a multimeter or battery tester to check voltage and state of charge. A healthy 12-volt battery should read around 12.6 volts when fully charged. If it drops below 12.4 volts, it may need charging or replacement.
Conclusion
So, how many amp hours does a car battery have? The answer depends on your vehicle, but most range from 40 to 100 Ah. This number tells you how long your battery can power your car’s electronics when the engine is off. While cold cranking amps get more attention, amp hours are equally important for reliability, especially if you use accessories frequently.
Understanding amp hours helps you choose the right battery, maintain it properly, and avoid unexpected breakdowns. Whether you drive a compact car or a heavy-duty truck, knowing your battery’s capacity ensures you’re prepared for any situation. So next time you’re shopping for a new battery, don’t just look at CCA — check the amp hour rating too. It could make all the difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does amp hour mean on a car battery?
Amp hour (Ah) measures how much energy a battery can store and deliver over time. It tells you how long the battery can power your car’s electronics before needing a recharge.
Is a higher amp hour battery better?
Not always. A higher Ah battery provides longer runtime, which is great for accessories or large vehicles. But it must fit your car and match your alternator’s charging capacity.
Can I replace a 50 Ah battery with a 70 Ah one?
Yes, as long as it fits physically and your vehicle’s electrical system can handle it. Most cars can accept a slightly higher Ah battery without issues.
How long will a 50 Ah battery last with the engine off?
It depends on the load. A 50 Ah battery can power a 10-watt light for about 60 hours, but high-draw devices like stereos will drain it much faster.
Do cold temperatures reduce amp hours?
Yes, cold weather slows chemical reactions in the battery, reducing its effective capacity by 20–50% in freezing conditions.
How often should I check my battery’s amp hour capacity?
You can’t measure Ah directly at home, but regular voltage checks and load tests every 6–12 months help assess overall health and performance.






