How Long Can a Car Battery Last Without Being Used

A car battery can last anywhere from 1 to 6 months without being used, depending on its age, type, and environmental conditions. Even when a vehicle sits idle, small electrical loads and natural discharge slowly drain the battery—understanding this helps you avoid unexpected dead starts.
Have you ever gone to start your car after it’s been sitting in the garage for a few weeks—only to hear that dreaded clicking sound? You turn the key, nothing happens, and suddenly you’re stuck. It’s frustrating, especially when you thought the battery was fine. The truth is, car batteries don’t like being ignored. Even when your car isn’t running, the battery is still working—just not in the way you might expect.
So, how long can a car battery actually last without being used? The short answer: it depends. On average, a healthy, fully charged car battery can sit unused for about 1 to 6 months before it dies. But that range is wide for a reason. Factors like battery age, type, temperature, and even the electronics in your car all play a role. If your car has a lot of modern features—like keyless entry, alarms, or onboard computers—it might drain the battery faster than an older model with fewer gadgets.
Understanding how and why batteries lose charge when not in use can save you time, money, and a lot of stress. Whether you’re storing a classic car for the winter, leaving a second vehicle unused for months, or just going on a long trip, knowing how to care for your battery is essential. In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about how long a car battery can last without being used, what causes it to die, and how to keep it alive—even when your car is sitting still.
In This Article
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 📑 Table of Contents
- 3 How Car Batteries Lose Charge Over Time
- 4 Factors That Affect How Long a Battery Lasts Unused
- 5 How Long Different Batteries Last Without Use
- 6 Signs Your Battery Is Dying from Inactivity
- 7 How to Extend Battery Life During Storage
- 8 When to Replace a Battery Before Storage
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
- 10.1 How long can a car battery sit without being driven?
- 10.2 Will a car battery die if not used for a month?
- 10.3 Can I leave my car unused for 3 months?
- 10.4 Does temperature affect how long a battery lasts unused?
- 10.5 What’s the best way to store a car battery long-term?
- 10.6 Can a dead battery from inactivity be recharged?
Key Takeaways
- Battery lifespan varies: Most car batteries last 1–6 months when unused, with newer batteries lasting longer than older ones.
- Parasitic drain matters: Modern cars have electronics that draw small amounts of power even when off, accelerating battery drain.
- Temperature plays a role: Extreme heat or cold can reduce battery life—storage in a cool, dry place helps.
- Battery type affects longevity: AGM and lithium-ion batteries typically hold a charge longer than traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Maintenance is key: Using a trickle charger or battery maintainer can extend battery life during long storage periods.
- Regular checks help: Testing voltage every few weeks ensures you catch low charge before it becomes a problem.
- Age is a major factor: Batteries older than 3–4 years lose charge faster and may not recover after long inactivity.
📑 Table of Contents
How Car Batteries Lose Charge Over Time
Even when your car is off, the battery isn’t completely idle. It’s still supplying small amounts of power to various systems—a phenomenon known as “parasitic drain.” This includes things like the clock, security system, alarm, and even some onboard computers that stay active to monitor vehicle status. While each of these draws only a tiny amount of current, over time, they can slowly drain the battery.
On top of that, all batteries naturally lose charge through a process called “self-discharge.” This happens because of internal chemical reactions that occur even when the battery isn’t connected to anything. In ideal conditions, a healthy lead-acid car battery might lose about 1% of its charge per day. That means in 30 days, it could lose up to 30% of its capacity. If it starts at 12.6 volts (fully charged), it could drop to around 12.0 volts—still enough to start most cars. But after two or three months, that voltage could fall below 11.8 volts, making it difficult or impossible to start the engine.
What Is Parasitic Drain?
Parasitic drain refers to the small electrical loads that continue to draw power from the battery when the car is off. Think of it like a slow leak in a tire—it’s not enough to notice right away, but over time, it adds up. Modern vehicles are especially prone to this because they’re packed with electronics. Features like remote start, GPS tracking, infotainment systems, and even tire pressure monitors all need a small amount of power to stay “awake” and ready.
For example, if your car has a built-in security system that sends alerts to your phone, it’s constantly communicating with satellites and cellular networks—even when parked. That uses energy. Similarly, some cars keep the climate control system in a “ready” state so it can pre-cool or pre-heat the cabin when you approach. All of these conveniences come at a cost: your battery’s charge.
Self-Discharge: The Silent Killer
Self-discharge is a natural part of how batteries work. It’s not caused by anything you did wrong—it’s just chemistry. In a lead-acid battery, the lead plates and sulfuric acid electrolyte slowly react over time, even when disconnected. This reaction reduces the battery’s state of charge.
The rate of self-discharge depends on the battery’s design and age. A brand-new battery might lose only 0.5% to 1% per day, while an older or poorly maintained one could lose 2% or more. Temperature also plays a big role. Batteries self-discharge faster in warm environments. For instance, a battery stored in a 90°F (32°C) garage might lose charge twice as fast as one kept in a 60°F (15°C) basement.
Factors That Affect How Long a Battery Lasts Unused

Visual guide about How Long Can a Car Battery Last Without Being Used
Image source: lirp.cdn-website.com
Not all batteries are created equal—and not all storage conditions are the same. Several key factors determine how long your car battery will last without being used. Understanding these can help you make smarter decisions about vehicle storage and battery care.
Battery Age and Condition
This is probably the most important factor. A brand-new battery (less than a year old) will hold its charge much longer than one that’s 3 or 4 years old. As batteries age, their internal components degrade. The lead plates corrode, the electrolyte evaporates, and the overall capacity drops. An older battery might start strong but lose charge rapidly when not in use.
For example, a 2-year-old battery might last 3–4 months without use, while a 5-year-old one could die in just 1–2 months. If your battery is already showing signs of weakness—like slow cranking or dim lights—it’s even more likely to fail when left unused.
Type of Battery
Not all car batteries are the same. The three most common types are:
– **Flooded lead-acid (standard):** The most common and affordable. These require maintenance (like checking water levels) and self-discharge faster.
– **Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM):** More advanced, sealed, and resistant to vibration. AGM batteries hold a charge longer and are often used in luxury or performance vehicles.
– **Lithium-ion:** Lightweight and long-lasting, but more expensive. Common in electric and hybrid vehicles. They have very low self-discharge rates.
AGM and lithium-ion batteries can last significantly longer without use—sometimes up to 6–12 months—thanks to their superior chemistry and lower self-discharge rates.
Temperature and Climate
Temperature has a huge impact on battery life. Extreme heat accelerates chemical reactions, increasing self-discharge. Cold temperatures slow reactions but can reduce the battery’s ability to deliver power when needed.
Storing a car in a hot garage (above 80°F/27°C) can cut battery life in half compared to a cool, climate-controlled space. Conversely, freezing temperatures (below 32°F/0°C) don’t speed up discharge much, but they make it harder for the battery to start the engine—even if it’s still charged.
Ideally, store your car in a garage or covered area where temperatures stay between 50°F and 70°F (10°C–21°C).
Vehicle Electronics and Features
The more “smart” features your car has, the more it will drain the battery when off. A basic 1990s sedan with minimal electronics might barely draw any power when parked. But a 2023 SUV with adaptive cruise control, lane assist, and a built-in Wi-Fi hotspot? That’s a different story.
These systems often stay in a low-power “sleep” mode, waiting for input. Over weeks or months, that adds up. If your car has a dashcam hardwired to the battery, a GPS tracker, or aftermarket alarms, those can also contribute to faster drain.
State of Charge When Stored
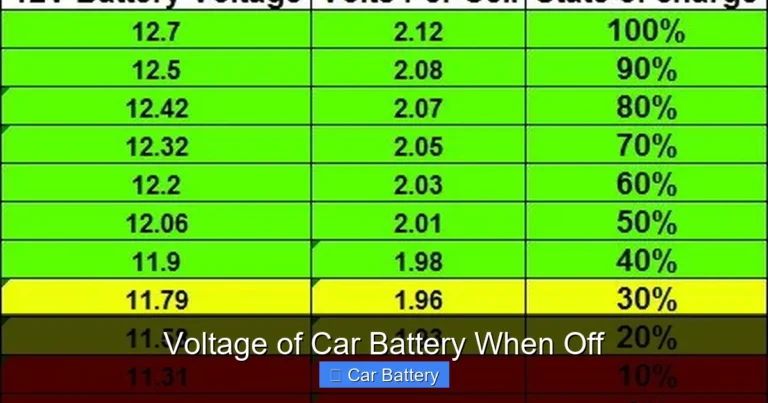
How charged your battery is when you park the car matters a lot. A battery stored at 100% charge will last much longer than one stored at 50%. Ideally, you should fully charge the battery before long-term storage. You can do this by driving the car for 30 minutes or using a battery charger.
A fully charged 12-volt battery reads about 12.6–12.7 volts. If it drops below 12.4 volts, it’s considered partially discharged. Below 12.0 volts, it’s deeply discharged—and may not recover.
How Long Different Batteries Last Without Use

Visual guide about How Long Can a Car Battery Last Without Being Used
Image source: compressorlab.com
Now that we’ve covered the factors, let’s look at real-world estimates. Here’s how long you can expect different types of batteries to last when the car isn’t used:
Standard Lead-Acid Batteries
– **New (0–1 year old):** 3–6 months
– **Mid-life (2–3 years old):** 2–4 months
– **Old (4+ years old):** 1–2 months
These are the most common batteries in gasoline-powered cars. They’re reliable but not designed for long-term storage without maintenance.
AGM Batteries
– **New:** 6–12 months
– **Mid-life:** 4–8 months
– **Old:** 2–4 months
AGM batteries are sealed, maintenance-free, and better at holding a charge. They’re ideal for vehicles that sit for long periods, like classic cars or RVs.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
– **New:** 12+ months
– **Mid-life:** 8–12 months
– **Old:** 6–8 months
Found in hybrids and EVs, lithium-ion batteries have very low self-discharge rates. However, they often have complex battery management systems that may draw small amounts of power to monitor cell health.
Deep-Cycle Batteries
Used in RVs, boats, and golf carts, deep-cycle batteries are designed to be discharged and recharged repeatedly. They can last 4–8 months without use, depending on age and type.
Signs Your Battery Is Dying from Inactivity

Visual guide about How Long Can a Car Battery Last Without Being Used
Image source: carbatterygeek.co.uk
You might not realize your battery is struggling until it’s too late. But there are warning signs to watch for—especially if your car has been sitting.
Slow Engine Crank
When you turn the key, the engine turns over slowly—like it’s struggling to start. This is one of the earliest signs of a weak battery. If it takes longer than usual to start, or if the starter sounds sluggish, the battery may be low.
Dim Lights and Electrical Issues
Headlights, interior lights, or dashboard lights that appear dimmer than usual can indicate low voltage. You might also notice that power windows, locks, or the radio respond slowly or not at all.
Clicking Sound When Starting
A rapid clicking noise when you turn the key usually means the battery doesn’t have enough power to engage the starter. This is a classic sign of a dead or nearly dead battery.
Battery Warning Light
If the battery or charging system warning light comes on the dashboard, it could mean the battery isn’t holding a charge. This is more common after the car has been started, but it can happen if the battery is old or damaged.
Swollen or Leaking Battery Case
In extreme cases, a battery that’s been deeply discharged or exposed to heat may swell or leak. This is a serious issue and means the battery should be replaced immediately.
How to Extend Battery Life During Storage
The good news? You don’t have to accept a dead battery after long storage. With a few simple steps, you can keep your battery healthy—even when your car isn’t moving.
Use a Trickle Charger or Battery Maintainer
A trickle charger slowly feeds power to the battery to keep it fully charged. It’s like a slow drip of energy that counters self-discharge and parasitic drain. Modern “smart” chargers (also called maintainers) are even better—they monitor the battery and only charge when needed, preventing overcharging.
For example, the Battery Tender Plus or NOCO Genius series are popular choices. Plug it in once a month, or better yet, leave it connected during long storage. Most can stay plugged in indefinitely without damaging the battery.
Disconnect the Battery
If you’re not using a charger, disconnecting the negative terminal can reduce parasitic drain. This stops most electronics from drawing power. However, it’s not perfect—some systems (like the ECU) may still draw a tiny amount of current.
Also, disconnecting the battery may reset your radio presets, clock, or navigation system. Some cars even require a code to restart the radio afterward.
Start the Car Regularly
If you can, start the car every 2–3 weeks and let it run for 15–20 minutes. This allows the alternator to recharge the battery. But be careful: idling alone may not fully recharge a deeply discharged battery. Driving the car for 30 minutes is better.
Store in a Cool, Dry Place
As mentioned earlier, temperature matters. Store your car in a garage or shaded area. Avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. If possible, use a car cover to reduce heat buildup.
Check Battery Voltage Monthly
Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage every few weeks. A healthy battery should read:
– 12.6–12.7 volts: Fully charged
– 12.4 volts: 75% charged
– 12.2 volts: 50% charged
– 12.0 volts or below: Needs charging
If it drops below 12.4 volts, plug in a charger.
Consider a Battery Cut-Off Switch
For long-term storage, a battery disconnect switch can completely cut power to the vehicle. It’s a simple device that installs on the negative terminal and allows you to physically disconnect the battery with the flip of a switch. This eliminates parasitic drain entirely.
When to Replace a Battery Before Storage
Sometimes, the best way to avoid a dead battery is to replace it before storing the car—especially if it’s old or showing signs of weakness.
Age Matters
Most car batteries last 3–5 years. If yours is approaching or past that age, consider replacing it before long storage. A new battery will hold a charge much better and give you peace of mind.
Performance Issues
If your car has been slow to start, even when used regularly, the battery may be nearing the end of its life. Don’t wait for it to fail in storage—replace it proactively.
Visible Damage
Check for cracks, leaks, or corrosion on the terminals. White or blue powder around the terminals is a sign of corrosion and can interfere with charging. Clean it with a baking soda and water solution, but if the battery case is damaged, replace it.
Failed Load Test
A load test measures how well the battery holds up under demand. Many auto parts stores offer free load testing. If the battery fails, it’s time for a new one.
Conclusion
So, how long can a car battery last without being used? The answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. A new, well-maintained battery in a cool garage might last 6 months or more. An old battery in a hot driveway could die in just a few weeks. But by understanding the factors at play—like parasitic drain, self-discharge, temperature, and battery type—you can take control.
The key is preparation. Whether you’re storing a classic car, leaving a second vehicle unused, or just going on vacation, a little planning goes a long way. Use a battery maintainer, check the voltage regularly, and consider replacing old batteries before they fail. With these tips, you can avoid the frustration of a dead battery and keep your car ready to go—no matter how long it’s been sitting.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can a car battery sit without being driven?
A car battery can typically sit unused for 1 to 6 months before it dies, depending on its age, type, and storage conditions. Newer batteries and those in cool environments last longer.
Will a car battery die if not used for a month?
Not necessarily. A healthy, fully charged battery can last a month without use. However, older batteries or those in hot climates may lose significant charge in that time.
Can I leave my car unused for 3 months?
Yes, but you should take precautions. Use a battery maintainer, disconnect the battery, or start the car every few weeks to keep the battery charged.
Does temperature affect how long a battery lasts unused?
Yes. Heat speeds up self-discharge, while cold reduces starting power. Storing your car in a cool, dry place helps extend battery life.
What’s the best way to store a car battery long-term?
Use a smart battery maintainer, store the car in a cool place, and check the voltage monthly. For very long storage, consider a battery disconnect switch.
Can a dead battery from inactivity be recharged?
Often, yes—if it hasn’t been dead for too long. Use a battery charger to slowly recharge it. However, deeply discharged or old batteries may not recover fully.