How Many Amps to Charge a Car Battery

Charging your car battery with the right number of amps is crucial for safety and battery health. Most car batteries charge best between 2 to 10 amps, depending on size and condition. Using too many amps can damage the battery, while too few may take too long.
In This Article
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 📑 Table of Contents
- 3 Understanding Car Battery Basics
- 4 How Many Amps to Charge a Car Battery: The Ideal Range
- 5 Factors That Affect Charging Amperage
- 6 Step-by-Step Guide to Charging Your Car Battery
- 7 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 8 When to Replace Instead of Recharge
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
- 10.1 Can I charge a car battery with a 2-amp charger?
- 10.2 Is it safe to charge a car battery at 10 amps?
- 10.3 How long does it take to charge a car battery at 6 amps?
- 10.4 Can I overcharge a car battery?
- 10.5 Should I disconnect the battery before charging?
- 10.6 Can I charge a car battery while it’s still in the car?
Key Takeaways
- Use 2 to 10 amps for standard car batteries: This range ensures safe, efficient charging without overheating or damage.
- Smaller batteries need fewer amps: Motorcycle or lawn tractor batteries often require only 1 to 2 amps to avoid overcharging.
- Higher amps charge faster but risk damage: Fast charging at 10+ amps should only be used for jump-starting, not full recharging.
- Smart chargers adjust amps automatically: These devices monitor voltage and battery condition to deliver the optimal charge rate.
- Check your battery’s CCA rating: Cold Cranking Amps help determine the battery’s capacity and guide appropriate charging amperage.
- Never exceed 1/10th of the battery’s Ah rating: For a 48Ah battery, max safe charging is around 4.8 amps for long-term health.
- Monitor temperature during charging: Batteries should stay cool; if warm, reduce amps or pause charging.
📑 Table of Contents
Understanding Car Battery Basics
Car batteries are the unsung heroes of your vehicle. They power everything from the engine starter to the lights, radio, and climate control. Without a healthy battery, your car simply won’t start. But how do you keep it in top shape? One of the most important aspects is knowing how many amps to charge a car battery.
At its core, a car battery is a rechargeable lead-acid unit that stores electrical energy. It delivers a burst of power when you turn the key, then recharges while the engine runs. Over time, especially in cold weather or with frequent short trips, the battery can lose its charge. That’s when you need to plug in a charger.
But not all chargers are created equal. The key factor? Amperage—the amount of electrical current flowing into the battery. Too little, and it takes forever. Too much, and you risk frying the battery or causing dangerous gas buildup.
So, what’s the sweet spot? Most experts agree that charging at 2 to 10 amps is ideal for standard 12-volt car batteries. But the exact number depends on several factors, including battery size, age, temperature, and the type of charger you’re using.
What Are Amps and Why Do They Matter?
Amps, short for amperes, measure the flow of electric current. Think of it like water flowing through a hose—amps are how much water (current) is moving per second. When charging a battery, higher amps mean more current is being pushed into the battery, which can speed up the process.
But just like a garden hose can burst if the water pressure is too high, a battery can be damaged if too many amps are forced into it too quickly. Lead-acid batteries, which are common in cars, are especially sensitive to overcharging. Excessive current can cause the electrolyte to boil, plates to warp, and even lead to explosions in extreme cases.
That’s why understanding how many amps to charge a car battery isn’t just about convenience—it’s about safety and longevity.
Battery Capacity and Amp-Hour Ratings
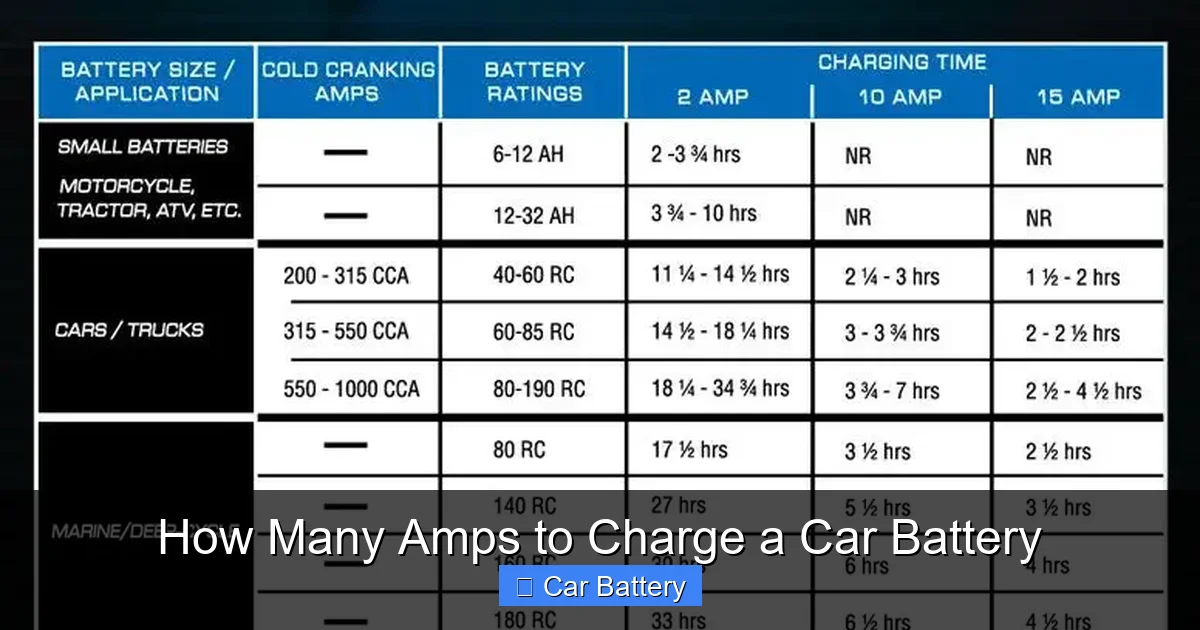
To choose the right charging amperage, you need to know your battery’s capacity. This is usually measured in amp-hours (Ah). A typical car battery might have a capacity of 40 to 70 Ah. This means it can theoretically deliver 1 amp for 40 to 70 hours, or 10 amps for 4 to 7 hours.
But here’s a rule of thumb: never charge a battery at more than 1/10th of its Ah rating. So for a 60Ah battery, the maximum safe charging rate is about 6 amps. This slow-and-steady approach helps prevent overheating and extends battery life.
For example, if you have a 48Ah battery, charging at 4 to 5 amps is ideal. It will take roughly 10 to 12 hours to fully recharge from a low state, but the battery will stay cool and healthy.
How Many Amps to Charge a Car Battery: The Ideal Range
Visual guide about How Many Amps to Charge a Car Battery
Image source: homebatterybank.com
Now that you understand the basics, let’s answer the big question: how many amps to charge a car battery?
For most standard 12-volt car batteries, the recommended charging rate is between 2 and 10 amps. But within that range, there are different use cases.
2 to 4 Amps: The Maintenance Charge
If your battery is only slightly discharged—say, from leaving the lights on overnight—a 2 to 4 amp charger is perfect. This slow charge is ideal for topping off the battery without stress. It’s also great for long-term storage, like when your car sits unused for weeks.
For example, if you have a classic car you only drive in summer, a 2-amp trickle charger can keep the battery ready all winter. It won’t overcharge, and it won’t drain your electricity bill.
4 to 6 Amps: The Balanced Charge
This is the sweet spot for most drivers. A 4 to 6 amp charger will recharge a moderately drained battery in 6 to 12 hours. It’s fast enough to be practical but gentle enough to protect the battery.
Let’s say your battery is at 50% charge. With a 5-amp charger, it should take about 6 hours to reach full capacity. That’s perfect for overnight charging—just plug it in before bed and wake up to a ready-to-go car.
6 to 10 Amps: The Fast Charge
Need a quick boost? A 6 to 10 amp charger can recharge a dead battery in 3 to 6 hours. This is useful if you’re in a hurry or stranded with a dead battery.
But caution: fast charging generates heat. If the battery gets warm to the touch, reduce the amps or pause charging. Also, avoid using high-amp chargers for regular maintenance—they’re best for emergencies.
Over 10 Amps: Jump-Start Only
Chargers above 10 amps are typically jump starters, not battery chargers. They deliver a high burst of current to get your engine running, but they’re not designed for full recharging.
Using a 20-amp or higher charger for a full charge can damage the battery, reduce its lifespan, and even pose a fire risk. Save the high amps for jump-starting, then switch to a lower setting or let the alternator finish the job.
Factors That Affect Charging Amperage

Visual guide about How Many Amps to Charge a Car Battery
Image source: motor.elfotograma.com
While 2 to 10 amps is a good general rule, several factors can influence the ideal charging rate.
Battery Size and Type
Not all car batteries are the same. Larger vehicles like trucks or SUVs may have higher-capacity batteries (70Ah or more), which can handle slightly higher amps. Smaller batteries, like those in motorcycles or lawn mowers, should be charged at 1 to 2 amps to avoid damage.
Also, battery chemistry matters. Most cars use flooded lead-acid batteries, but some newer models have AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) or gel batteries. These require specific charging profiles—often lower amps and precise voltage control. Using the wrong charger can ruin an AGM battery in one session.
Battery Age and Condition
An old or damaged battery may not accept a charge efficiently. Sulfation—a buildup of lead sulfate crystals—can reduce capacity and increase resistance. In such cases, a slow charge (2 to 4 amps) is better, as it gives the battery time to absorb the current.
If your battery is more than 5 years old or has visible cracks, leaks, or a swollen case, it may be time for a replacement. Charging a failing battery with high amps can accelerate its demise.
Temperature and Environment
Cold weather slows chemical reactions in the battery, making it harder to charge. In winter, you may need to use a slightly higher amp setting (within safe limits) or use a charger with a cold-weather mode.
Conversely, hot weather increases the risk of overheating. If you’re charging in direct sunlight or a hot garage, stick to lower amps and monitor the battery temperature.
A good rule: if the battery feels warm, stop charging and let it cool down. Never charge a hot battery.
Charger Type and Features
Not all chargers are equal. Basic models deliver a constant current, which can overcharge if left unattended. Smart chargers, on the other hand, adjust the amps automatically based on the battery’s state.
For example, a smart charger might start at 6 amps, then drop to 2 amps as the battery nears full charge. Some even have desulfation modes to revive weak batteries.
Investing in a quality smart charger can save you money in the long run by extending battery life and preventing overcharging.
Step-by-Step Guide to Charging Your Car Battery

Visual guide about How Many Amps to Charge a Car Battery
Image source: compressorlab.com
Now that you know how many amps to charge a car battery, let’s walk through the process.
Step 1: Safety First
Before touching the battery, turn off the engine and remove the keys. Wear safety glasses and gloves. Batteries contain sulfuric acid and can release explosive hydrogen gas.
Work in a well-ventilated area, away from sparks or open flames.
Step 2: Locate and Inspect the Battery
Open the hood and find the battery. Check for corrosion (white or green powder on the terminals), leaks, or damage. If you see corrosion, clean it with a mixture of baking soda and water, then rinse with clean water.
Step 3: Choose the Right Charger and Amp Setting
Select a charger compatible with your battery type (flooded, AGM, etc.). Set the amps based on the battery’s capacity and condition.
For a standard 60Ah battery, start with 4 to 6 amps. If it’s deeply discharged, you can go up to 8 amps, but monitor closely.
Step 4: Connect the Charger
Attach the red (positive) clamp to the positive terminal (+) and the black (negative) clamp to the negative terminal (-). Make sure the connections are tight and secure.
Never reverse the polarity—it can damage the battery and the charger.
Step 5: Start Charging
Turn on the charger and let it run. Most smart chargers will display the charging progress. If using a manual charger, check the battery voltage periodically with a multimeter.
A fully charged 12-volt battery should read around 12.6 to 12.8 volts when the engine is off.
Step 6: Monitor and Disconnect
Don’t leave the charger unattended for long periods. Once the battery is fully charged (usually indicated by a green light or voltage reading), turn off the charger and disconnect the clamps in reverse order: black first, then red.
Step 7: Test the Battery
Start the car to ensure it runs smoothly. If the engine cranks slowly or won’t start, the battery may still be weak or the alternator could be faulty.
Consider having the battery tested at an auto parts store for a professional assessment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the right knowledge, it’s easy to make mistakes when charging a car battery.
Using Too Many Amps
One of the biggest errors is cranking up the amps to charge faster. While it might seem efficient, high amps can overheat the battery, warp the plates, and shorten its lifespan.
Stick to the 1/10th rule: for a 50Ah battery, max 5 amps.
Leaving the Charger On Too Long
Overcharging is just as bad as undercharging. It can cause the electrolyte to boil, leading to gas buildup and potential explosion.
Use a smart charger with an automatic shut-off feature, or set a timer if using a manual model.
Ignoring Battery Type
Using a standard charger on an AGM or gel battery can ruin it. These batteries require lower voltage and precise charging curves.
Always check your owner’s manual or battery label to confirm the type.
Charging in Extreme Temperatures
Charging a frozen battery can cause it to crack. Never charge a battery below 32°F (0°C) unless it’s specifically designed for cold charging.
Similarly, avoid charging in direct sunlight or hot environments without monitoring.
Not Cleaning Terminals
Corroded terminals increase resistance and reduce charging efficiency. Clean them regularly to ensure a solid connection.
When to Replace Instead of Recharge
Sometimes, no amount of charging will save a battery. Here are signs it’s time to replace:
- The battery is more than 5 years old.
- It fails a load test at an auto shop.
- It won’t hold a charge after a full night of charging.
- You see physical damage like cracks or swelling.
- The car struggles to start, even after charging.
A new battery costs $100 to $200, but it’s cheaper than repeated jump-starts or roadside assistance calls.
Conclusion
Knowing how many amps to charge a car battery is essential for every driver. The ideal range is 2 to 10 amps, with 4 to 6 amps being the best balance of speed and safety for most situations. Always match the charging rate to your battery’s capacity, type, and condition.
Use a smart charger when possible, monitor the process, and avoid common mistakes like overcharging or using the wrong settings. With proper care, your car battery can last 4 to 6 years—or even longer.
Remember, a little knowledge goes a long way. By charging your battery the right way, you’ll save money, avoid breakdowns, and keep your car running smoothly for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I charge a car battery with a 2-amp charger?
Yes, a 2-amp charger is safe and effective for maintaining or slowly recharging a car battery. It’s ideal for trickle charging and long-term storage.
Is it safe to charge a car battery at 10 amps?
Charging at 10 amps is safe for short periods, especially for deeply discharged batteries. But avoid using this rate for long-term charging, as it can generate excess heat.
How long does it take to charge a car battery at 6 amps?
A 6-amp charger typically takes 6 to 10 hours to fully recharge a standard 60Ah car battery, depending on how depleted it was.
Can I overcharge a car battery?
Yes, overcharging can damage the battery, cause electrolyte loss, and even lead to explosions. Always use a smart charger or monitor the process closely.
Should I disconnect the battery before charging?
It’s not always necessary, but disconnecting the battery can protect your car’s electronics. If you’re unsure, consult your owner’s manual or use a smart charger designed for in-vehicle charging.
Can I charge a car battery while it’s still in the car?
Yes, most modern chargers are safe to use with the battery installed. Just ensure the charger is compatible and follow safety precautions to avoid sparks near the battery.






