How Many Volts Is a Car Battery

A standard car battery operates at 12 volts, which is essential for starting your engine and powering electrical systems. While a fully charged battery reads around 12.6 volts at rest, it can drop to 12 volts or lower when the engine is off, indicating the need for a recharge or replacement. Understanding these voltage levels helps maintain optimal vehicle performance and prevents unexpected breakdowns.
In This Article
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 📑 Table of Contents
- 3 How Many Volts Is a Car Battery
- 4 What Is Voltage and Why Does It Matter for Car Batteries?
- 5 Standard Car Battery Voltage: What You Need to Know
- 6 How to Measure Your Car Battery’s Voltage
- 7 Factors That Affect Car Battery Voltage
- 8 When to Replace Your Car Battery Based on Voltage
- 9 Car Battery Voltage Reference Table
- 10 Conclusion: Stay Powered, Stay Safe
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways
- A fully charged car battery delivers 12.6 volts: this indicates optimal health and readiness to start your vehicle.
- 12.4 volts or below suggests a weak battery: consider testing or recharging to avoid unexpected failure.
- Cranking requires 9.6 volts minimum: anything lower may prevent your engine from starting.
- Check voltage with a multimeter: a simple test can reveal your battery’s true condition.
- Recharge if voltage drops below 12.4 volts: maintain charge to extend battery life and reliability.
- Extreme temperatures affect voltage output: monitor performance more closely in hot or cold climates.
📑 Table of Contents
- How Many Volts Is a Car Battery
- What Is Voltage and Why Does It Matter for Car Batteries?
- Standard Car Battery Voltage: What You Need to Know
- How to Measure Your Car Battery’s Voltage
- Factors That Affect Car Battery Voltage
- When to Replace Your Car Battery Based on Voltage
- Car Battery Voltage Reference Table
- Conclusion: Stay Powered, Stay Safe
How Many Volts Is a Car Battery
Have you ever been stranded in a parking lot, turning the key in your ignition only to hear that dreaded clicking sound—or worse, complete silence? I’ve been there. It’s frustrating, especially when you’re already running late. That moment usually leads to one big question: Is it the battery? And if it is, the next logical thought is, “How many volts is a car battery supposed to have anyway?”
Understanding your car battery’s voltage isn’t just for mechanics or gearheads—it’s essential knowledge for every driver. Whether you’re trying to jump-start your vehicle, deciding when to replace the battery, or simply curious about how your car starts, knowing the basics of voltage can save you time, money, and stress. In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about car battery voltage in simple, everyday language. No technical jargon, no confusing diagrams—just clear, practical info to help you feel confident behind the wheel.
What Is Voltage and Why Does It Matter for Car Batteries?
Let’s start with the basics: what exactly is voltage? Think of voltage as the “push” that moves electricity through a circuit. It’s the electrical pressure that gets things moving—like water pressure in a hose. Without enough voltage, your car’s electrical system simply can’t function. The battery provides this voltage to start the engine, power the lights, run the radio, and support all the electronics in modern vehicles.

Visual guide about How Many Volts Is a Car Battery
Image source: thepowerall.com
Voltage in Simple Terms
Voltage is measured in volts (V), and it represents the potential energy difference between two points in an electrical circuit. In a car battery, this energy is stored chemically and released as electricity when needed. A fully charged car battery typically delivers around 12.6 volts when the engine is off. But here’s the catch: that number drops when the engine is running, when the battery is old, or when it’s been sitting in cold weather.
Why Voltage Matters for Your Car
Your car relies on a steady supply of voltage to operate. The starter motor, for example, needs a strong burst of power—usually around 10–12 volts—to turn the engine over. If the voltage is too low, the starter won’t have enough power to crank the engine, and you’ll be stuck. Similarly, low voltage can cause dim headlights, slow power windows, or a malfunctioning infotainment system.
Even small voltage drops can signal bigger problems. For instance, if your battery reads 12.0 volts or less when the car is off, it may be nearing the end of its life. Regularly checking your battery’s voltage can help you catch issues early and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Real-Life Example: The Cold Morning Start
Imagine it’s a chilly winter morning. You get in your car, turn the key, and the engine struggles to start. The lights flicker, and the radio resets. This is a classic sign of low battery voltage. Cold temperatures slow down the chemical reactions inside the battery, reducing its ability to deliver power. A healthy battery should still provide enough voltage to start the car, but an aging or weak battery might not.
In this scenario, knowing your battery’s voltage can help you decide whether to jump-start it, replace it, or just give it time to warm up. It’s a small detail that can make a big difference in your day.
Standard Car Battery Voltage: What You Need to Know
Now that we understand what voltage is and why it matters, let’s get to the heart of the question: how many volts is a car battery? The short answer is that most standard car batteries are 12-volt systems. But there’s more to the story than just that number.

Visual guide about How Many Volts Is a Car Battery
Image source: cdn.shopifycdn.net
The 12-Volt Standard
Virtually all gasoline-powered passenger vehicles on the road today use a 12-volt electrical system. This includes cars, SUVs, light trucks, and even most motorcycles. The 12-volt standard has been around for decades because it provides a good balance between power and safety. It’s high enough to run the starter motor and electronics, but low enough to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
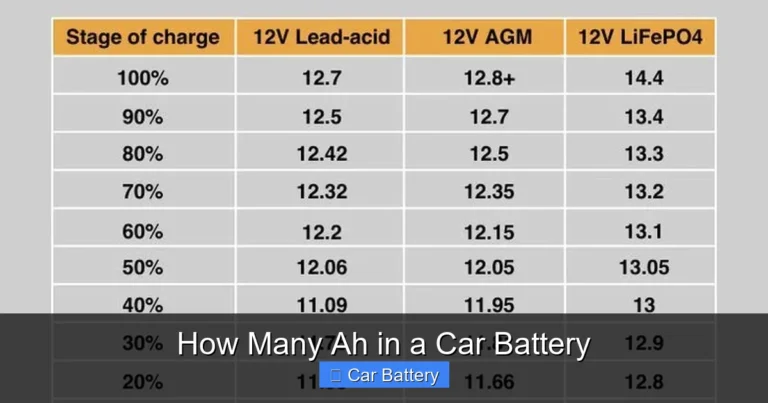
But here’s a key detail: a “12-volt” battery isn’t actually delivering exactly 12 volts all the time. When fully charged and at rest (meaning the engine is off and the battery hasn’t been used for a few hours), a healthy car battery should read around 12.6 volts. This is because each of the six cells in the battery produces about 2.1 volts, and 6 × 2.1 = 12.6 volts.
Voltage Under Different Conditions
The voltage of your car battery changes depending on its state of charge and whether the engine is running. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Fully charged (engine off): 12.6 volts
- 75% charged: 12.4 volts
- 50% charged: 12.2 volts
- 25% charged: 12.0 volts
- Fully discharged: Below 11.9 volts
When the engine is running, the alternator takes over and charges the battery, so the voltage typically rises to between 13.7 and 14.7 volts. This higher voltage ensures the battery stays charged and powers all the car’s systems while driving.
Why 12 Volts? A Bit of History
You might wonder why cars use 12 volts instead of, say, 6 or 24. The answer lies in automotive history. Early cars used 6-volt systems, but as engines grew larger and more electronics were added, 6 volts wasn’t enough to reliably start the engine or power accessories. By the 1950s, the industry shifted to 12 volts, and it’s remained the standard ever since.
Some larger vehicles, like heavy-duty trucks and buses, use 24-volt systems. These systems use two 12-volt batteries connected in series to double the voltage. This provides more starting power for large diesel engines. But for the average driver, 12 volts is the norm.
How to Measure Your Car Battery’s Voltage
Now that you know what voltage to expect, the next step is learning how to measure it. Checking your car battery’s voltage is easier than you might think—and it’s a skill every driver should have. All you need is a simple tool called a multimeter, which you can buy for under $20 at most hardware or auto parts stores.

Visual guide about How Many Volts Is a Car Battery
Image source: thepowerfacts.com
Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring Voltage
Here’s how to check your battery’s voltage safely and accurately:
- Turn off the engine and all electrical accessories. This includes lights, radio, air conditioning, and anything else that draws power.
- Open the hood and locate the battery. It’s usually a rectangular box with two cables attached—one red (positive) and one black (negative).
- Set your multimeter to DC voltage (usually marked as “V~” or “V–”). Make sure it’s set to a range that includes 12 volts (most auto-ranging multimeters will do this automatically).
- Touch the red probe to the positive terminal (+) and the black probe to the negative terminal (–). Be careful not to let the probes touch each other or any metal parts.
- Read the display. A healthy battery should show around 12.6 volts. If it’s lower, the battery may be partially discharged.
For the most accurate reading, let the car sit for at least an hour before testing. This allows the surface charge—a temporary voltage boost from recent use—to dissipate.
What the Numbers Mean
Once you’ve measured the voltage, here’s how to interpret the results:
- 12.6 volts or higher: The battery is fully charged and in good condition.
- 12.4–12.5 volts: The battery is about 75% charged. It should still start the car, but consider recharging it soon.
- 12.2–12.3 volts: The battery is about 50% charged. It may struggle to start the engine, especially in cold weather.
- 12.0–12.1 volts: The battery is low and needs recharging. It’s at risk of failing.
- Below 11.9 volts: The battery is deeply discharged and may be damaged. It likely won’t start the car.
If your battery consistently reads below 12.4 volts, it’s a sign that it’s aging or there’s a problem with the charging system (like a faulty alternator).
Pro Tip: Test After Driving
It’s also helpful to test the battery voltage while the engine is running. With the car on, the multimeter should read between 13.7 and 14.7 volts. If it’s lower, the alternator may not be charging the battery properly. If it’s higher than 15 volts, there could be an overcharging issue, which can damage the battery over time.
Factors That Affect Car Battery Voltage
Your car battery’s voltage isn’t constant—it fluctuates based on several factors. Understanding these can help you maintain your battery and avoid surprises.
Temperature and Climate
Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can impact battery performance. Cold weather slows down the chemical reactions inside the battery, reducing its ability to deliver voltage. That’s why cars are harder to start in winter. In fact, a battery can lose up to 35% of its power at 32°F (0°C) and up to 60% at 0°F (-18°C).
On the flip side, hot weather can cause the battery to overheat and lose electrolyte through evaporation. Over time, this can shorten the battery’s lifespan. If you live in a hot climate, it’s especially important to check your battery regularly and keep it clean and well-ventilated.
Battery Age and Condition
Like any component, car batteries wear out over time. Most last between 3 and 5 years, depending on usage and climate. As a battery ages, its internal plates degrade, reducing its capacity to hold a charge. This means the voltage drops more quickly, even when the battery is fully charged.
If your battery is more than three years old and you’re noticing slow starts or dim lights, it’s a good idea to have it tested. Many auto parts stores offer free battery testing, so you don’t even need a multimeter.
Electrical Load and Usage Patterns
How you use your car also affects battery voltage. Short trips, for example, don’t give the alternator enough time to fully recharge the battery. Over time, this can lead to a gradual loss of charge. Similarly, using power-hungry accessories like heated seats, high-powered audio systems, or phone chargers can drain the battery faster.
If you frequently drive short distances or leave electronics on when the engine is off, consider investing in a battery maintainer or trickle charger. These devices keep the battery topped up when the car isn’t in use.
Parasitic Drain
Sometimes, a battery loses voltage even when the car is off. This is called parasitic drain, and it happens when something in the car continues to draw power—like a faulty relay, a stuck glove box light, or an aftermarket alarm system. A small drain (under 50 milliamps) is normal, but anything higher can kill the battery overnight.
If your battery keeps dying for no apparent reason, a mechanic can perform a parasitic drain test to find the culprit.
When to Replace Your Car Battery Based on Voltage
Knowing your battery’s voltage is one thing—knowing when to replace it is another. While voltage readings give you a good indication of health, they’re not the only factor. Still, they’re a great starting point.
Signs It’s Time for a New Battery
Here are some common signs that your battery may need replacing, based on voltage and other symptoms:
- Voltage below 12.4 volts when the engine is off: This suggests the battery is not holding a full charge.
- Slow engine crank: If the engine turns over slowly or hesitates, the battery may not have enough power.
- Check engine or battery warning light: These lights can indicate a charging system problem, including a weak battery.
- Swollen or bloated battery case: This is a sign of overheating or overcharging and means the battery is failing.
- Old age: If your battery is more than 4 years old, it’s wise to start planning for a replacement.
Testing Before You Buy
Before spending money on a new battery, get a professional test. Many auto parts stores will test your battery and charging system for free. They’ll check the voltage, load test the battery (to see how it performs under stress), and inspect the alternator.
A load test is especially important because it simulates the demand of starting the engine. A battery might show 12.6 volts at rest but fail under load, which means it can’t deliver the power needed to start the car.
Choosing the Right Replacement
When it’s time to replace your battery, don’t just grab the cheapest one. Look for a battery with the correct group size (which fits your car), cold cranking amps (CCA) rating (higher is better for cold climates), and warranty. A good-quality battery may cost more upfront but will last longer and perform better.
And remember: even a new battery needs proper maintenance. Keep the terminals clean, avoid deep discharges, and drive regularly to keep it charged.
Car Battery Voltage Reference Table
To make it easy to understand your battery’s condition at a glance, here’s a quick reference table showing voltage levels and what they mean:
| Voltage (Engine Off) | State of Charge | Battery Condition |
|---|---|---|
| 12.6 volts or higher | 100% charged | Excellent – battery is healthy and fully charged |
| 12.4 – 12.5 volts | 75% charged | Good – battery should start the car, but consider recharging |
| 12.2 – 12.3 volts | 50% charged | Fair – battery may struggle in cold weather; recharge soon |
| 12.0 – 12.1 volts | 25% charged | Poor – battery is low and needs immediate attention |
| Below 11.9 volts | Fully discharged | Critical – battery is likely damaged and won’t start the car |
This table is a handy tool to keep in your glove box or save on your phone. Just remember to test the battery after it’s been sitting for at least an hour for the most accurate reading.
Conclusion: Stay Powered, Stay Safe
So, how many volts is a car battery? The answer is simple: most car batteries are 12-volt systems, but a healthy one should read around 12.6 volts when fully charged and at rest. That number drops as the battery loses charge, and understanding those changes can help you avoid being stranded with a dead car.
Checking your battery’s voltage is a quick, easy way to stay on top of your car’s health. With just a multimeter and a few minutes, you can spot problems early, extend your battery’s life, and save yourself from costly repairs or emergency calls. Whether you’re a daily commuter or a weekend driver, this small habit can make a big difference.
Remember, your car battery is more than just a power source—it’s the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system. Treat it well, keep an eye on its voltage, and it’ll keep you moving mile after mile. And the next time you turn the key and the engine roars to life, you’ll know exactly why.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many volts is a car battery?
A standard car battery typically has 12 volts. This is the most common voltage for vehicles with internal combustion engines.
Can a car battery have more than 12 volts?
Yes, some heavy-duty or commercial vehicles use 24-volt systems, especially large trucks and buses. These systems provide more power for starting large engines and running auxiliary equipment.
Is a 6-volt battery used in any cars?
6-volt batteries were common in older vehicles made before the 1950s. Modern cars almost exclusively use 12-volt batteries for better performance and compatibility with electrical systems.
What happens if a car battery drops below 12 volts?
If a 12-volt car battery drops below 12 volts, it may struggle to start the engine. A reading below 11.8 volts often indicates the battery is discharged and may need recharging or replacement.
How can I check how many volts my car battery has?
You can use a multimeter to measure the voltage across the battery terminals. A healthy, fully charged 12-volt battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off.
Does the voltage change when the car is running?
Yes, when the engine is running, the alternator charges the battery, so voltage typically rises to 13.7 to 14.7 volts. This higher voltage ensures the battery stays charged while powering the vehicle’s electrical systems.